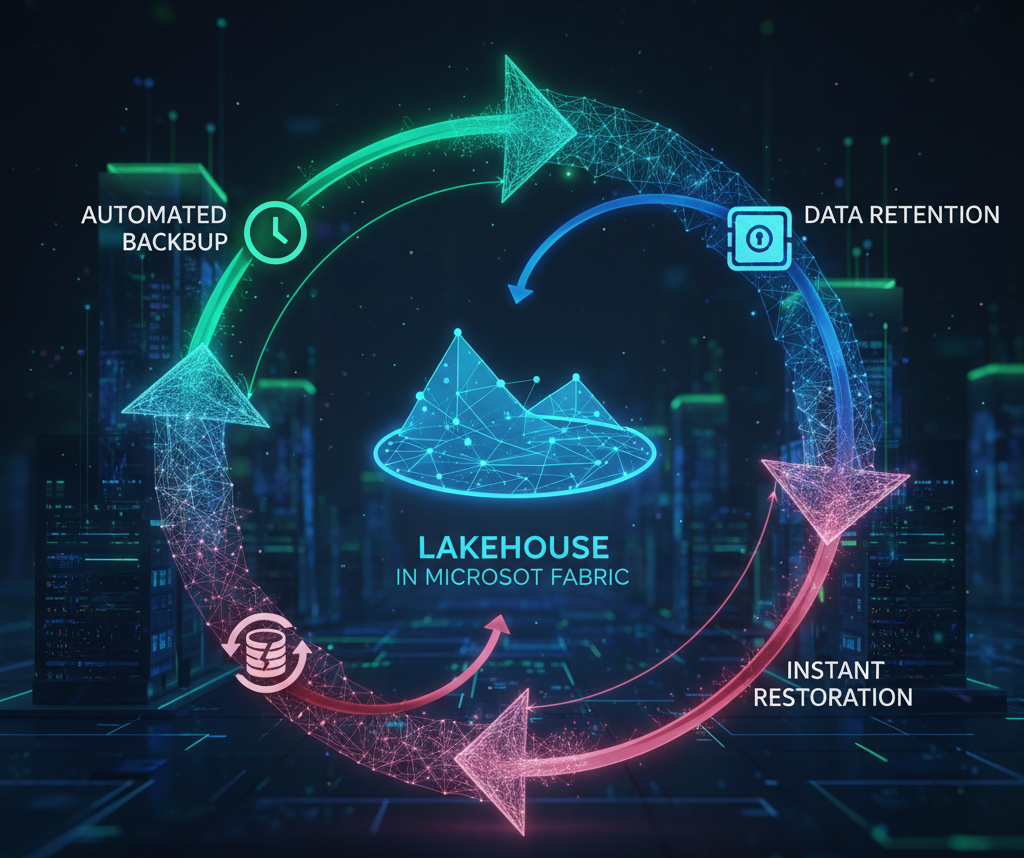
Data resilience is the foundation of every modern analytics platform. In Microsoft Fabric, implementing automated backup, retention, and restoration strategies is essential to strengthen data protection and ensure operational continuity.
While Microsoft Fabric includes built-in disaster recovery (DR) capabilities, these are not intended to address everyday operational issues such as data refresh failures, accidental deletions, or data corruption. To bridge these gaps, an automated backup and retention approach becomes critical—helping organizations maintain seamless operations and data reliability.
Note: The methods described here are not replacements for Microsoft Fabric’s disaster recovery features. Instead, they serve as a complementary layer to enhance resilience, streamline restoration, and minimize downtime through automation and proactive configurations.
Setting Up Backup and Retention Policies
Microsoft Fabric’s Lakehouse and OneLake architectures provide robust foundations for data management. However, to ensure durability and compliance, automated backup and retention policies must be thoughtfully designed.
Key Components:
- Daily Incremental Backups: Capture daily snapshots to minimize data loss and maintain version history.
- Retention Policy Configuration: Define retention tiers—daily, weekly, monthly, and yearly—to balance compliance requirements and storage efficiency.
- Automation via Notebooks: Utilize Fabric notebooks or scheduled Spark jobs to automate backup creation, enforce retention policies, and clean up obsolete data.
Automation Highlights:
- Backup Creation: Scheduled scripts trigger snapshot creation at defined intervals. For instance, Spark jobs leveraging APIs such as mssparkutils can efficiently copy and version datasets.
- Retention Enforcement: Policy-based automation ensures outdated backups are automatically purged while preserving those required for compliance or audits.
- Logging and Monitoring: Every backup, cleanup, and restoration task is logged for transparency, traceability, and audit-readiness.
Restoration: Recovering from Data Loss
Restoring data in Fabric can be performed at multiple levels—either the entire Lakehouse or specific tables—depending on the recovery need.
Restoration Best Practices:
- Restore data directly from automated snapshots or archived backups.
- Leverage structured logs to diagnose and resolve issues encountered during restoration.
- Minimize downtime by using predefined scripts or automation workflows that accelerate recovery and reduce manual intervention.
Why Automate Backup and Retention in Microsoft Fabric?
Automation introduces consistency, reliability, and efficiency—key pillars of a resilient data ecosystem.
Core Benefits:
- Data Integrity: Automated, incremental backups safeguard critical datasets against accidental loss or corruption.
- Operational Continuity: Rapid, scripted restorations minimize business disruption.
- Cost Optimization: Automated cleanup routines remove redundant backups, optimizing storage utilization.
- Scalability: Policy-driven automation scales effortlessly with expanding data volumes and evolving business needs.
Conclusion
Microsoft Fabric empowers organizations with a unified, intelligent data platform—but ensuring data durability and operational continuity requires more than built-in DR. By automating backup, retention, cleanup, and restoration processes, organizations can strengthen data resilience, minimize downtime, and maximize the business value of their Fabric investments.
In essence, automation transforms data protection from a reactive process into a proactive, scalable strategy—one that keeps pace with modern analytics demands and ensures the integrity of your most valuable asset: data.